Cellulite is a skin condition that primarily affects women. Around 80% to 90% of women develop cellulite at some stage in their lives. Unlike men, most women store excess fat around the hips, buttocks, thighs and lower abdomen. When the deposition of excess fat intensifies, the fat cells start to push upwards and into the deeper layers of our skin. On the outside, our skin starts to look lumpy and uneven. These dimples or depressions in our skin are known as cellulite.
Cellulite becomes more prominent with age and weight gain, but studies have shown that even people as young as teenagers and those who have a slim figure can develop cellulite due to other medical and environmental reasons such as genetic disorders, hormonal imbalances, and reduced oxygen level in the blood.
Cellulite is commonly visible on the buttocks and thighs. It can affect a woman’s appearance and lower her confidence level, especially if she is fond of wearing mini dresses and shorts.
How Does Collagen Affect Cellulite?
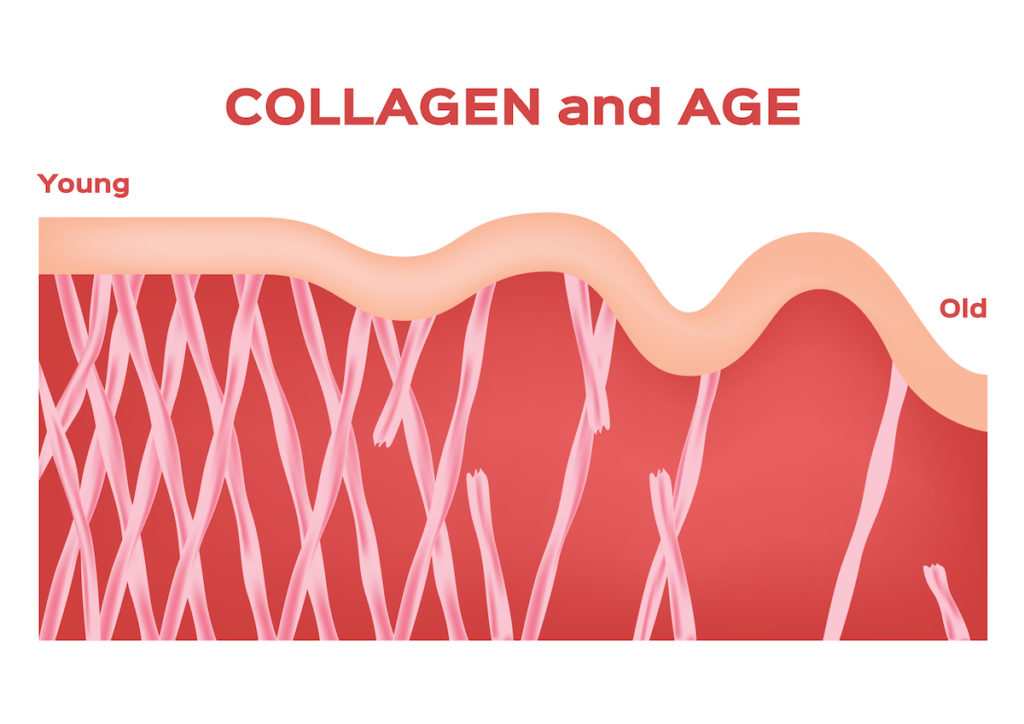
After the age of 20, our body produces 1% less collagen every year. This means that by the age of 35, your body will be producing 35% less collagen than it used to when you were in your teenage years.
Collagen is an essential protein that is produced by our body as a building block to form connective tissues, hair, nails, teeth, skin, blood vessels, cornea, ligaments, tendons, etc.
Due to its elastic nature, collagen supports the body’s normal functions like growth, expansion and contraction. When the collagen production in our body reduces with age, our skin becomes less elastic and thin. This is why when the fat cells push up against the dermal cells; the skin is unable to flex and push back the fat cells. The lumps of fat cells become more visible on the outside because the skin becomes thinner and gets easily pushed up.
Lower levels of collagen make the skin lose its elasticity and firmness. As a result, skin starts to sag, and cellulite becomes more apparent.
How to Restore Collagen and Reduce Cellulite?
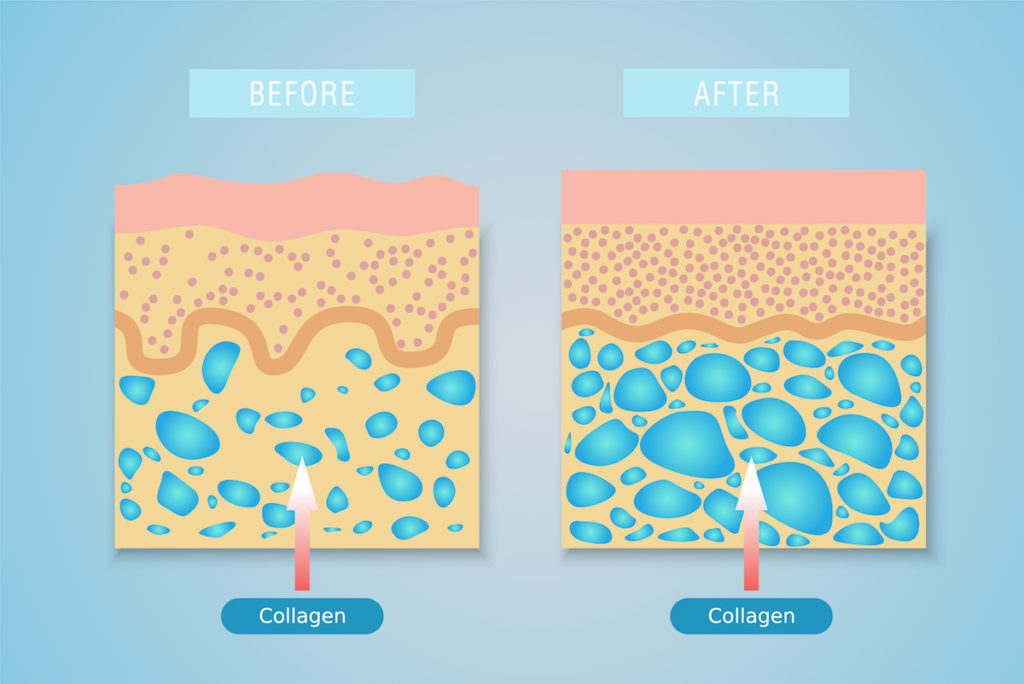
To increase the level of collagen in your body and reduce the appearance of cellulite, you should opt for radiofrequency treatment.
Radiofrequency treatment is a non-invasive treatment for cellulite reduction. During the radiofrequency treatment, an FDA-approved hand-held device or applicator will be used to gently massage the areas which have been affected by cellulite, such as your thighs and buttocks. The device produces radiofrequency waves and heat that help to break up and melt the fat cells from underneath the skin.
The liquefied fat is then either digested by the digestive enzymes and broken down into simple molecules for easy absorption, or if it is unneeded, it is transported to the body’s lymphatic system where it passes through the lymph nodes, and it expelled out of the body as a waste product.
With the removal of fat cells, the dermal cells fall back into their place. But because the radiofrequency waves and heat had damaged the surrounding skin cells in the process, the body produces collagen to repair these damaged cells. As the old skin cells are replaced with the new ones that have a higher volume of collagen, our skin regains its elasticity and firmness.
The overall effect of the radiofrequency treatment is as follows:
- Removes stubborn pockets of fat from the thighs and buttocks
- Reduces the appearance of cellulite
- Produces collagen
- It makes the skin thicker, tighter, firmer and smoother than before
- Contoured buttocks and thighs (lifts and tightens the saggy skin)
Some studies have shown that just by orally ingesting collagen peptides daily for over 6 months, there can be a significant reduction in the appearance of cellulite. This indicates that collagen has a direct positive effect on restoring the thickness and texture of the skin and making it less prone to cellulite.
Related Articles


How do I use a body contouring machine?



