We’re all familiar with the heavenly taste of chocolate cake, scrumptious donuts or creamy cheesecakes after a bad day at work (or on a random Tuesday)! For many, sweet treats are the go-to remedy after a breakup, when life gets too stressful or too boring! Hitting up your nearest pastry joint seems like the perfect idea for some comfort food.
Have you ever heard of the saying, “STRESSED spelled backward is DESSERTS”? Well, guess what, it’s true. When we become stressed, our blood sugar level drops along with our blood pressure. This deficiency of glucose in our bloodstream makes us crave desserts and sugary treats. And that’s when we start to binge-eat ice-creams, candy, milkshakes, pies and pudding!
What we seldom realize is that this momentary lapse of judgment can have long-term, adverse effects on our health because sugars cause inflammation and can derail not only our slim body goals but our overall general health, breeding the way for many chronic diseases.
HOW SUGARS CAUSE INFLAMMATION?
Several research studies have shown the causal effect of sugar on increased inflammation in our body. In a study conducted in 2018, it was found that people who consume MORE sugar in their diet are MORE prone to inflammation. Similarly, another study illustrated that people who consume LESS sugar had FEWER inflammation markers in their bodies.
Medical science has shown that insulin converts excess glucose molecules to fatty acids which are then stored as fat in the liver tissues. This process releases C-reactive proteins in our body, and these proteins cause inflammation. Moreover, in patients with diabetes, excess sugar intake causes insulin resistance, and this too leads to inflammation.
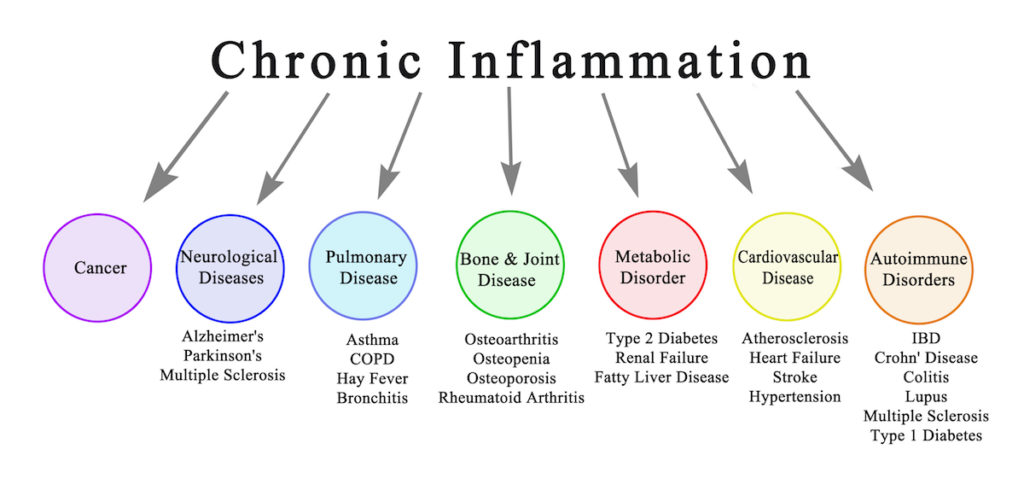
If left untreated, inflammation can cause our own immune system starts to attack our body cells. This can result in serious medical conditions like arthritis, cancer, heart diseases, and organ failures.
HOW DOES SUGAR DERAIL BODY GOALS?
Sugar can lead to obesity. The recommended intake of sugar is said to be 12 teaspoons per day or around 200 calories. But on average, Americans consume about 270 calories of sugar, which makes it around 17 teaspoons of sugar per day. The problem with sugars like glucose, sucrose, and fructose is that these are naturally present in our meals. Even a small bowl of fruit salad contains around 16-20 grams of sugar.
So, on a daily basis, you are consuming more sugar via your meals, fruit and vegetable salads, and beverages than you can keep track of. If, on top of that, you have a sweet tooth and cannot live without your daily desserts, then your body starts to store the excess glucose that you consumed as fat.
Insulin is a hormone that is present in our body and helps to convert excess glucose molecules into a complex chain of molecules known as fatty acids. These fatty acids reach other parts of our body and get stored as fat in the adipose tissues. When the accumulation of fat in our adipose tissues increases, our organ tissues become fatty, and as a result, we start to gain weight and become obese.
Researchers have found that people who consume more sugar than the recommended daily amount can gain 1.7 pounds of weight in less than 2 months. Another research study that confirmed the correlation between excess sugar intake and obesity found that Americans consume 300% more sugar than the recommended daily amount, and this is why two-thirds of the US population is either overweight or obese.
Sugar is a slow poison. It is addictive and can have serious implications on our physical and mental health. Some of the other adverse effects of consuming too much sugar may include:
- Tooth decay
- Depression
- Hypertension
- Inflammation of joints
- Heart Diseases
- Diabetes
- Autoimmune disorders
- Kidney damage
- Reduced sexual drive
- Cancer
- Wrinkles and saggy skin
So now the choice is yours. Will you go sugar-free or add one more cube of sugar to your tea?
Related Articles


How do I use a body contouring machine?



